Level39-based charity is developing Cancer Platform as a resource for those with a diagnosis and their loved ones that’s set to launch in 2026

Subscribe to our free Wharf Whispers newsletter here
We live in an unprecedented age of information.
Never before have so many people had access to such a wealth of content at the mere tap of a finger.
But with the vastness of a largely unregulated digital world comes the issue of quality.
With not only humans (who are bad enough) but AIs churning out swathes of answers, opinions and hallucinations as they whisper what it heard or saw, humanity is increasingly submerged in a sea of at best confusion and at worst falsehoods.
It’s not so very long ago that wellness blogger Belle Gibson fooled hundreds of thousands of followers and Apple with her tale of overcoming brain, blood, spleen, uterine and kidney cancers, mostly through exercise, healthy eating and a positive mindset.
In reality there’s no evidence the Australian social media personality was ever diagnosed with the disease – but that didn’t stop her developing an app, gaining widespread influence and being embraced by one of the world’s largest tech firms.
Her twisted story is especially relevant, given its use of cancer as a jumping off point.
About half of us will develop some form of the disease during our lives.

searching for information
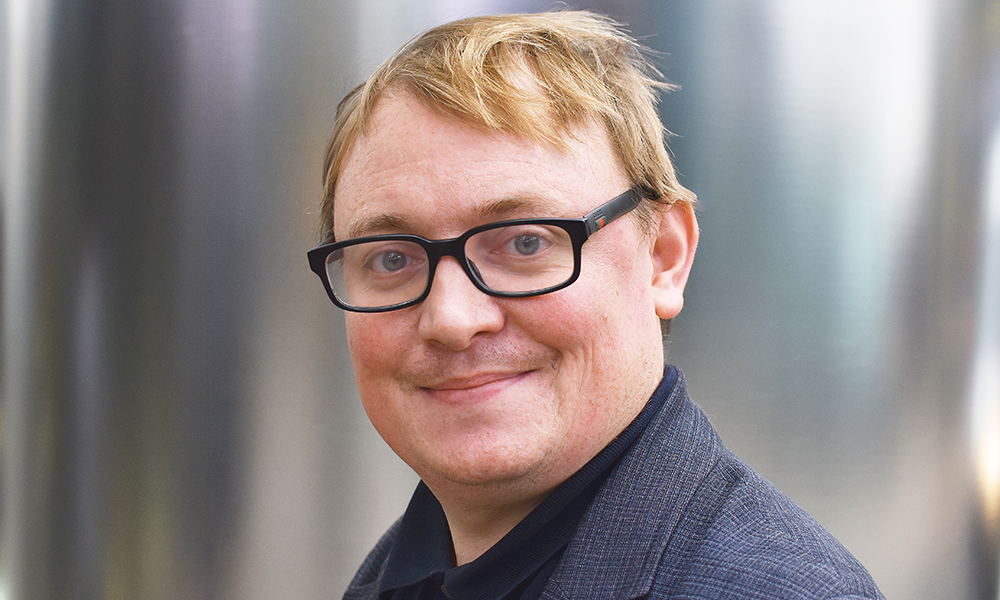
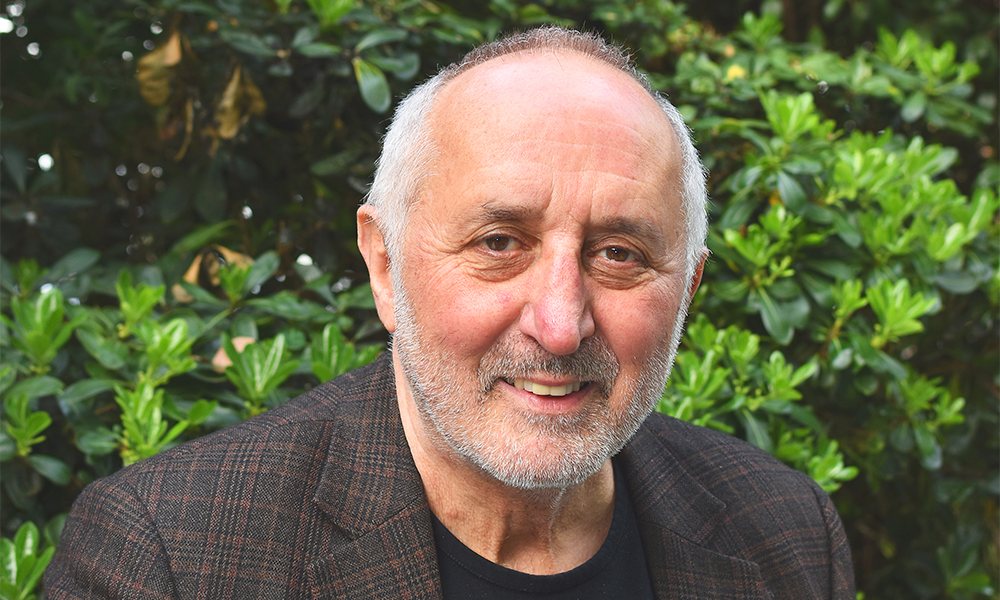
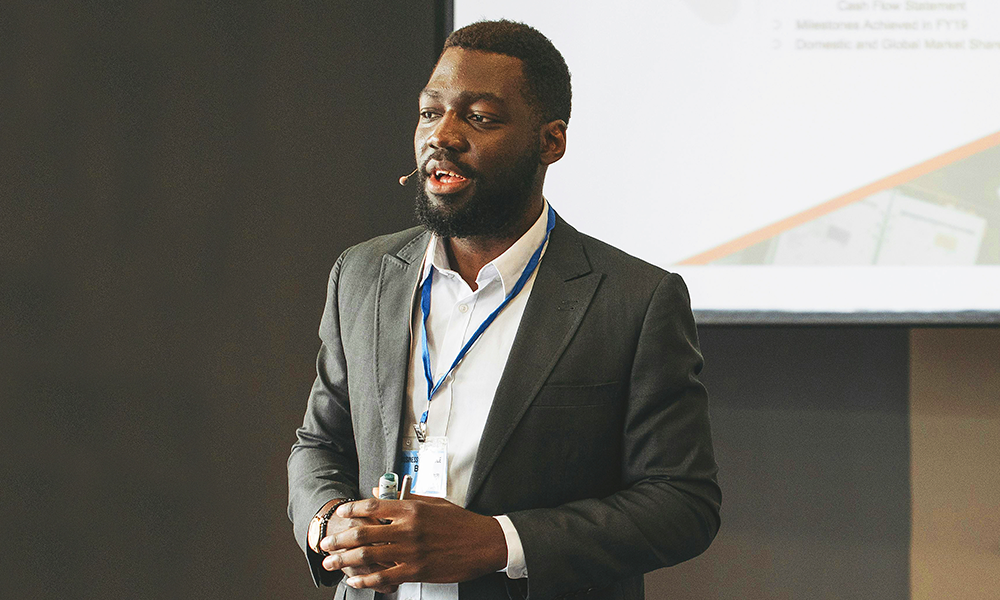
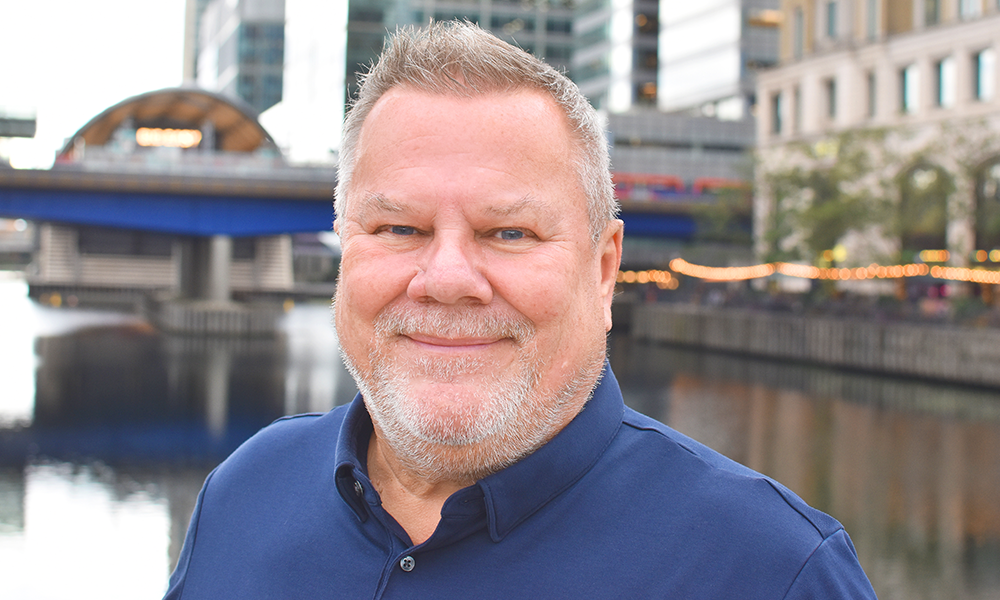
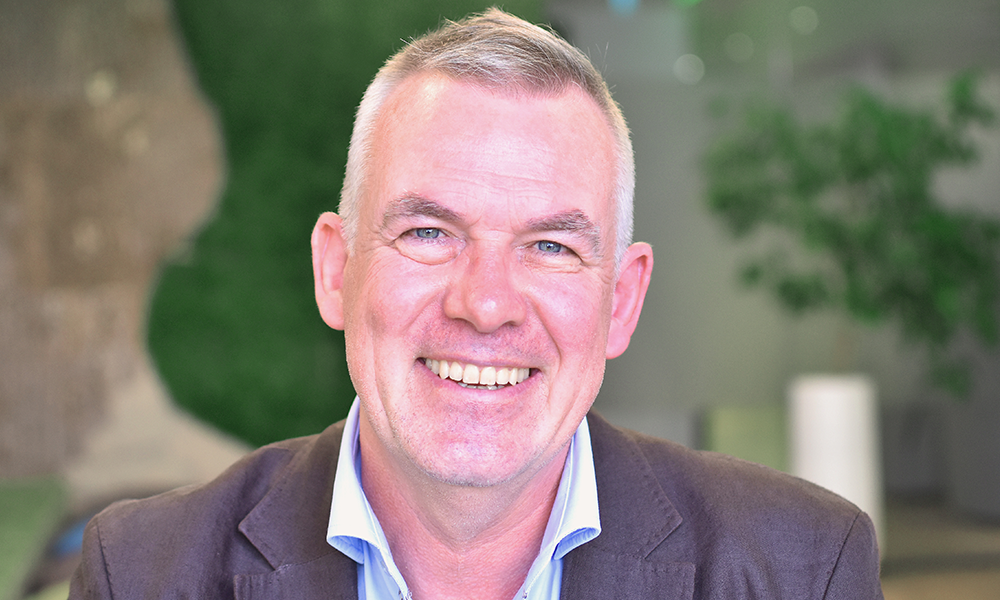
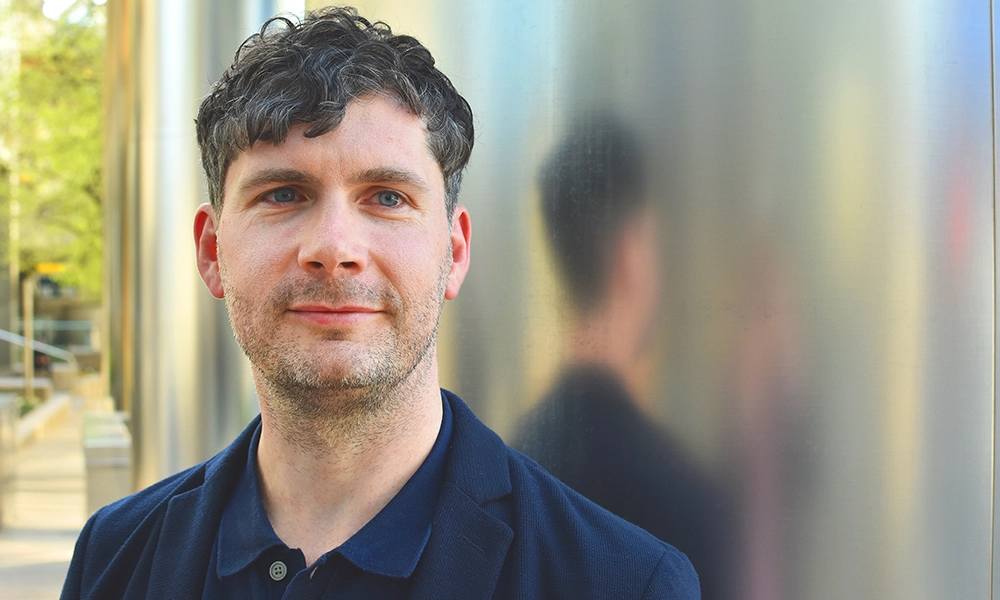
“At the point of diagnosis, the vast majority of people will go online to search for information, as do their loved ones,” said Daniel Woolf.
“But they can easily find themselves in the wrong place – TikTok or Instagram, for example.
“A short-form video of someone who is very charismatic may lead someone to go away and make life-changing decisions because they are looking for a glimmer of hope.
“But are they trustworthy?
“Something like one in three online sources is either misinformation or not pertinent to a particular individual’s diagnosis.”
That’s what the development of Cancer Platform is seeking to change.
“Sitting beneath the umbrella of the Cancer Awareness Trust – a charity based at tech community, Level39, in Canary Wharf – the mission is to create a free-to-use app which delivers expert information, stories and services.
As the organisation’s chief tech and data officer, it’s Daniel’s job to oversee the app’s development, a task he’s relishing after a long career in the NHS.
“I planned to be there for four weeks and ended up being there for 17 years,” he said.
“I’ve been an engineer, a data analyst and have directed a number of teams at regional and national level.
“But as I moved through the various national bodies, I found I couldn’t have the impact I wanted.
“There are so many layers and I felt insulated.
“With so many different governments the chairs were always being moved around.
“What I wanted to do was use technology to help improve people’s lives.
“The bureaucracy in the NHS was enormous and so, when it came time for a career change, I wanted something small with the feel of a startup where I could be hands-on, albeit in an organisation with huge ambition.”
the Cancer Awareness Trust’s ambitions
The Cancer Awareness Trust is aiming big.
Drawing funds and support from its creative brand Evamore Music – which has released works featuring the likes of Ozzy Osborne, Cillian Murphy, Glenn Close and the late Sinéad O’Connor – the organisation is supported by Canary Wharf Group, among many others, in its efforts to deliver Cancer Platform.
“The trust’s aim is to empower people to change the course of cancer,” said Daniel, who was born in Hoxton and grew up in east London.
“Having the artists, music, events and that creative spirit involved makes us unique – it’s very different from the technology side.
“With Cancer Platform we want to hold people’s hands through their journey after a diagnosis.
“We’re testing it this summer and we’re aiming to put it out there in 2026 and then to gradually build it up with more and more information.
“What we’re creating is a layer above the standard websites that are out there.
“Cancer Platform uses personalisation and AI to make the information highly relevant to each user.
“There is a lot of good information out there already, but it’s fragmented and often it’s left to the individual to find what’s relevant to them.
“Cancer Platform helps users to build up a scrapbook of information that helps them consolidate their knowledge and understanding from a trusted source.
“It’s about taking away the unpredictability of Dr Google.
“Cancer is complicated. Treatments may be available in certain regions but not in others. Ethnicity, background and age are also relevant.
“Our aim is to provide information and services that are relevant to each individual as well as relatable stories from people in similar situations, offering hopeful optimism where appropriate.
“A lot of medical information can sound cold and clinical – more about the cancer than the person.
“Our ambition is for people not to have to log-in initially.
“We want to build that trust first and some people might have a diagnosis they don’t wish to disclose – safeguarding is important to us and we won’t be selling their data.
“We also want people to be able to search for information that’s personalised to a degree, but then we’ll encourage people to sign up for an account so they can take the next steps and we can really hold their hands.
“They might come to Cancer Platform to ask about symptoms or a diagnosis and then what we’re doing in the background is pairing them up with relevant information, pulling it from trusted sources and feeding it back to them in an understandable way.
“The key thing is not just giving answers, but making sure we give them the right sources to guide people to specific charities. Then they are able to see the next steps.
“One of the things we’re trying to do is to inform people about the questions they should be asking when they next visit their oncologist such as whether they are entitled to a second opinion.
“Users will get responses, suggested prompts and stories of people like them so they can get an idea of what their own journey might be like.”
the process of assurance
Key to Cancer Platform’s aims will be ensuring the information it supplies to users is robust, accurate and clear.
This is one of the greatest challenges in its delivery and one Daniel and the team are already deeply engaged with.
“The assurance process is in development at the moment,” he said.
“It’s quite a new field. There are a number of academic papers, which are all looking at the area of trusted information.
“These include some principles and measures, which we’re then building our own assurance processes on top of as well as working with leading oncologists.
“We also have a team which is taking a granular approach in ensuring that the information we supply is accurate and comprehensive.
“For example, we have banks of questions from a wide array of sources, that say: ‘These questions are what people come to us to ask’.
“So we’ve taken those answers through our assurance process and then they’re assessed for their accuracy and fitness for purpose.
“It’s vital to get the balance right.
“We’ve got our oncology team working through that now and the results from them will show us what levers to pull next.
“Have we identified the gaps in our knowledge base?
“Do we need to tune the AI a different way to access and serve more information?”
a trusted source of information
Ultimately, the charity’s intention is for Cancer Platform to provide information on all forms of the disease, a project truly massive in its scope.
Initially, the plan is to focus on breast and prostate cancers before expanding out to other areas.
“Admittedly, our ambition is huge so it’s about constantly focussing on the next step,” said Daniel.
“A number of specific charities already exist in these areas, so we can build out from that and make sure it’s working for those groups of patients.
“It also helps us to co-design with those communities.
“One of the biggest challenges – because there are so many good ideas – is to make sure we’re hyper-focussed. That’s my job.
“Building a platform like this is hard but we’re at a crossroads moment.
“Until recently, much of the information we needed just wasn’t there but it is now.
“We want to make it available to people and to do that without selling their data. We’re a charity so there’s no profit motive.”
key details: Cancer Awareness Trust
You can find out more about the Cancer Awareness Trust, Cancer Platform and Evermore via the charity’s website.
Read more: Lina Stores is set to open its doors in Canary Wharf